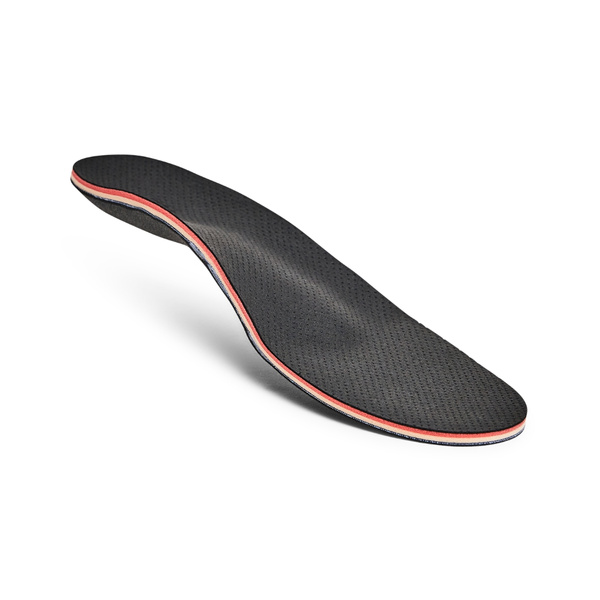
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome or medial tibial periostitis, are a common overuse injury often experienced by runners. They are characterized by pain along the front or inner side of the lower leg. To treat and prevent shin splints, it is beneficial to wear shoes with orthopedic inserts that offer excellent support and cushioning.
What Are Shin Splints?
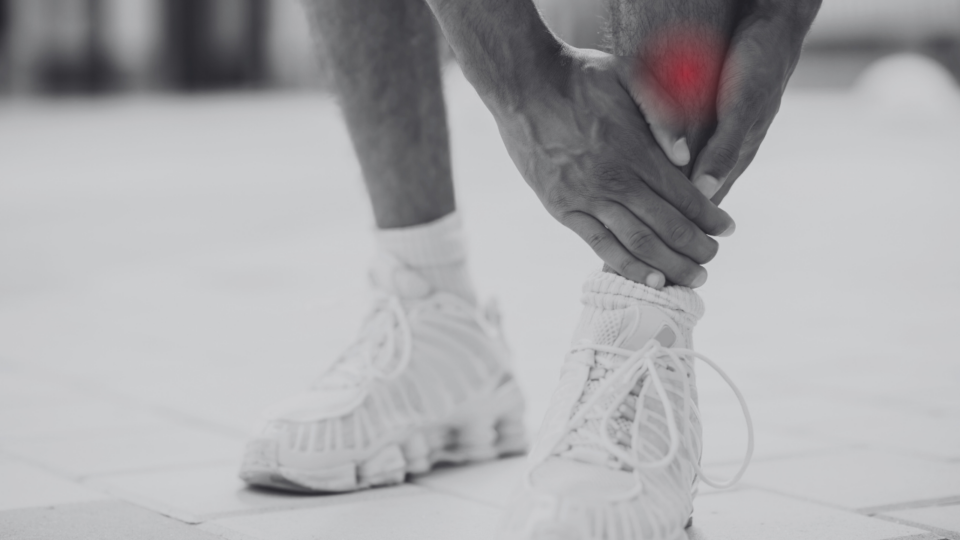
Shin splints are a common overuse injury resulting from overstressing the muscles and tendons in the lower leg. This condition often arises during intense training or when you’ve increased your activity levels, making it particularly common among athletes and dancers. Shin splints typically develop if you engage in more physical activity than you’re used to, such as running or walking longer distances than normal.
Symptoms of Shin Splints
Shin splints typically cause pain on the inside or front of the lower leg. You might feel stiffness after periods of inactivity, and the initial steps when you first get up can be painful, though this pain often lessens with gentle movement. Additionally, a dull ache in the leg may develop in the evening after a full day of activity.
Common symptoms of shin splints include:
- Pain along the front, inside, and edge of the shinbone
- Pain during physical activity, particularly while running or jumping
- Intense pain that may force you to stop the activity
- Pain that improves with rest
- Tenderness and swelling around the shinbone
The pain associated with shin splints can be:
- Sharp and stabbing or dull and throbbing
- Present both during and after exercise
- Worsened by touching the affected area
Why You Get Shin Splints
Shin splints occur due to overstraining the muscles, tendons, and other tissues inside the shinbone. They often arise with sudden changes in physical activity, such as:
- Increased training frequency: You train more days per week than before.
- Longer workouts: You run longer distances than you’re used to.
- Increased intensity: You start running on hills or other challenging surfaces.
You are at higher risk for shin splints if you:
- Walk or run on hard surfaces
- Have high or low arches
- Have flat feet combined with misalignments
- Wear shoes without adequate support and cushioning or worn-out shoes